Overview
C-Mannosylation is a unique type of protein glycosylation. A C-C bond is formed between the C1 atom of an α-mannose and the C2 atom of the indole ring of a tryptophan residue via mannosyl-transferases.
| pKa | NC | Loss | Gain | Deltamass | H | AA | UV-Spec | Pattern |
| – | No | H | C6H11O5 | Av: 162.1408 M: 162.0528 | 0 | W | – | W(?=..W) |
In-depth mechanism
Glycosylations of proteins are one of the most common and widespread post-translational modifications. Best known are N– and O-glycosylations. More than 25 years ago, a new type of glycosylation, C-mannosylation, was discovered. C-Mannosylation differs fundamentally from previously described types of glycosylation. A C-C bond is formed between the C1 atom of an α-mannose and the C2 atom of the indole ring of a tryptophan residue. The reaction is catalysed by mannosyltransferases, which use dolychyl-phosphate-mannose as donor for the mannose moiety1,2. Dolychyl-phosphate-mannose is formed from GDP-mannose and dolichol-phosphate on the cytosolic side of the endoplasmatic reticulum3. The mechanism of C-mannosylation is shownin figure 1.
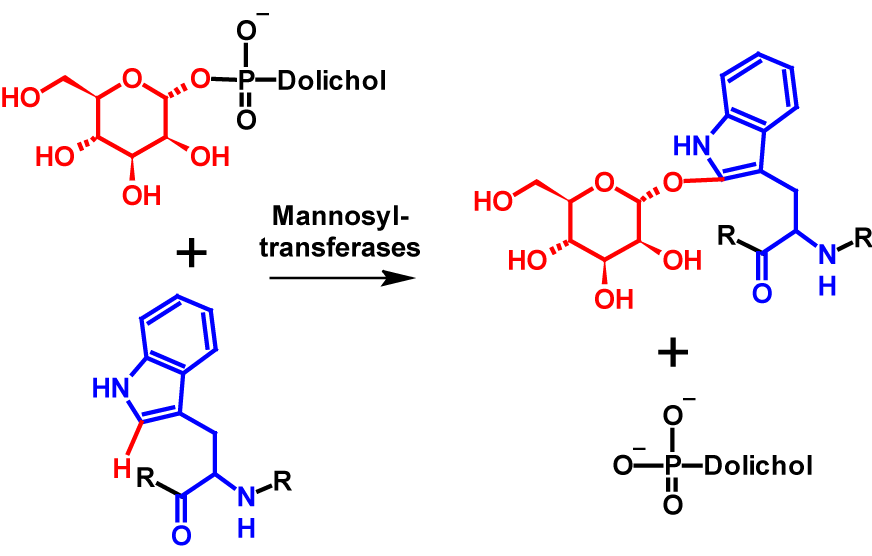
Mannosyltransferases recognize W-X-X-W motifs and C-mannosylate the first tryptophan in the sequence. However, this pattern can vary slightly from organism to organism2. The exchange of the second tryptophan residue for other amino acids strongly restricts or even completely prevents C-mannosylation. The influence of the two amino acids between the tryptophan residues is still the subject of current studies1. The W-X-X-W motif occurs in many proteins, which suggests that C-mannosylation is a common an widespread post-translational modification. The function of C-mannosylation is still largely unknown today1,2. The hydrophobicity of a protein is not altered by C-mannosylation.
References
- 1.Furmanek A, Hofsteenge J. Protein C-mannosylation: facts and questions. Acta biochimica Polonica. 2000;47:781–789.
- 2.Lafite P, Daniellou R. Rare and unusual glycosylation of peptides and proteins. Natural Product Reports. 2012;29:729–738. doi:10.1039/C2NP20030A
- 3.Maeda Y, Kinoshita T. Dolichol-phosphate mannose synthase: structure, function and regulation. Biochimica et biophysica acta. 2008;1780:861–868. doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2008.03.005